Did you know that, thanks to reverse logistics, 93% packaging plastic of pesticides sold in Brazil have adequate environmental disposal?
A fundamental instrument for various productive sectors, it brings environmental benefits, social and economic for the entire society.
Therefore, learn more about the concept of reverse logistics, how the cycle works, its types and current Brazilian legislation on the subject.
What is reverse logistics?
First of all, reverse logistics is a set of actions and means for collecting, dismantling, processing and returning products to companies for reuse in productive chain or for appropriate environmental disposal.
Furthermore, it completes the traditional cycle, which takes products from suppliers to intermediate or final customers.
In this sense, the reverse logistics cycle involves consumers, traders, manufacturers and importers, collector and recycling cooperatives and public authorities.
What is the difference between selective collection and reverse logistics?
Selective collection is the process of collecting solid waste previously separated according to its composition. This way, this waste can be recycled or not.
Thus, we can carry out collection door-to-door or in voluntary delivery points (PEV).
Reverse logistics, meanwhile, will take products back to the company to reuse or dispose of properly.
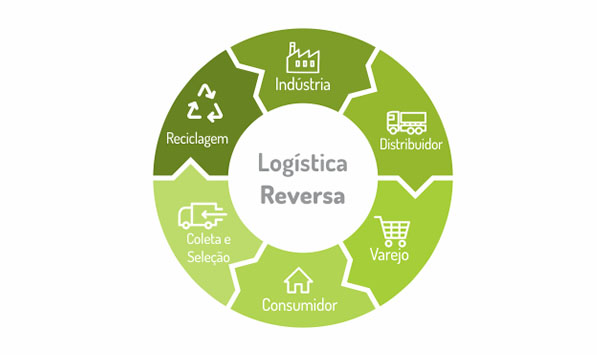
How does the reverse logistics cycle work?
The logistics cycle begins with the consumer, who is responsible for disposing of waste correctly and in the locations established by their systems.
The private sector is responsible for the environmentally appropriate management of solid waste, its reincorporation into the production chain, as well as the rational use of materials.
Finally, the public authorities monitor the process and create awareness and education for correct disposal.
What is the main objective of reverse logistics?
The main objective of reverse logistics for companies is to meet three fundamentals: economic, environmental or legal.
Regarding the environment, the company that adopts this strategy gains the green, environmentally responsible company seal, which generates more competitiveness and a good reputation.
Meanwhile, on the economic side, the concept can help reduce costs and obtain profits with the recovery of products or part of them,
Therefore, adapting to current legislation is another factor that makes companies use this process, especially those that comply with current law, in the case of Brazil.
What are the benefits of reverse logistics?
The benefits of reverse logistics are countless, both for the environment and the economy.
According to the Solid Waste Management Information System (BELL), the Ministry of the Environment, find out some of its benefits:
- Encouraging reuse, recycling and waste treatment;
- Reduction of CO2 in the atmosphere, which can contain global warming;
- Sharing responsibility for solid waste between the public and private sectors and civil society;
- Increased efficiency in the use of natural resources;
- Encouragement of reuse, recycling and treatment of solid waste;
- Increasing the useful life of landfills through the reallocation of waste that can return to the production chain, thus avoiding soil contamination.
- Development of environmentally sustainable products.
What are the main types of reverse logistics?
There are three main types: after-sales, post-consumer and reuse.
In after-sales, an item is returned because it is defective or does not meet the consumer's expectations (defect, wrong size, malfunction, etc.). In these cases, the customer returns the product to the company, which may or may not use it.
Post-consumer reverse logistics refers to the disposal and reuse of waste produced by the consumption of a certain product.
Thus, in post-consumption, which is gaining more and more followers, the waste resulting from the consumption of a product is destined for recycling, reuse or correct disposal.
An everyday example is the returnable bottles, which can be returned to exchange stations to be reused a few more times.
Another example are fluorescent lamps, which, after being discarded at collection points, are sent to the recycling industry for the production of ceramics, for example.
Meanwhile, reuse consists of selling, through auctions, items that would otherwise be discarded, such as furniture, cars, electronics, books, etc. This way, companies can profit from sales.
Practical examples of reverse logistics
An example of the application of reverse logistics is the implementation of the General Packaging Reverse Logistics System.
The objective of this system is to dispose of packaging in an environmentally friendly way to recycle and reuse.
It works as follows: the consumer separates the post-consumer packaging. This way, the city's collection system will collect this material and take it to cooperatives and associations of collectors and recycling, where they will carry out the screening.
Then, wholesale recyclables resell the material to recyclers, who recycle the material. Once recycled, the material reaches industries that manufacture products with recycled materials. Companies produce, distribute and sell products using recycled materials.
Reverse logistics in Brazil
The concept in Brazil is supported by Law 12.305/10, which established the National Solid Waste Policy (PNRS).
And at the beginning of 2022, the National Program of Reverse Logistics, which aims to coordinate and integrate its different systems.
Article 33 of the law establishes that manufacturers, importers, distributors and traders of pesticides, batteries, tires, lubricating oils, lamps and electronic products are obliged to implement reverse logistics systems.
According to data from the Ministry of the Environment, between 2019 and 2020, 470 tons of electronics were collected at 3,100 collection points across the country.
In addition to electronics, Brazil collected 275 thousand tons of batteries, which were recycled, generating 144 thousand tons of lead, avoiding contamination of the soil and groundwater.
Finally, Brazil also holds the title of world record holder for collecting and recycling aluminum cans. In 2020, 31 billion aluminum cans were recycled in the country.
Discover Já Fui Bag, iFood reverse logistics action


